With terms like LPN, LVN, RN, BSN, MD, DPT and CNA, the healthcare field has no shortage of career-related acronyms. It can be rather confusing just trying to keep them all straight.
For starters, students who consider a nursing career often pursue a bachelor’s degree. However, the field offers several opportunities that do not require a four-year commitment. This allows graduates to begin earning a living and acquiring professional experience with less time and educational cost.
A Practical Nursing certificate only requires about a year of study, while an Associate Degree in Nursing (ADN) requires about two years of study. There is also the option of pursuing an education in Medical Assisting, which can be completed in as few as nine months for a certificate or in as few as 16 months for an associate degree.
Now here is where it can get confusing. While Practical Nursing programs may prepare students to become a licensed practical nurse (LPN), ADN programs can lead to becoming a registered nurse (RN). LPNs assist RNs and physicians since the responsibilities for LPNs include collecting samples, taking vital signs, providing patient care, and reporting patient statuses to RNs. LPNs also typically work in long-term care facilities, hospitals, or physicians’ offices.
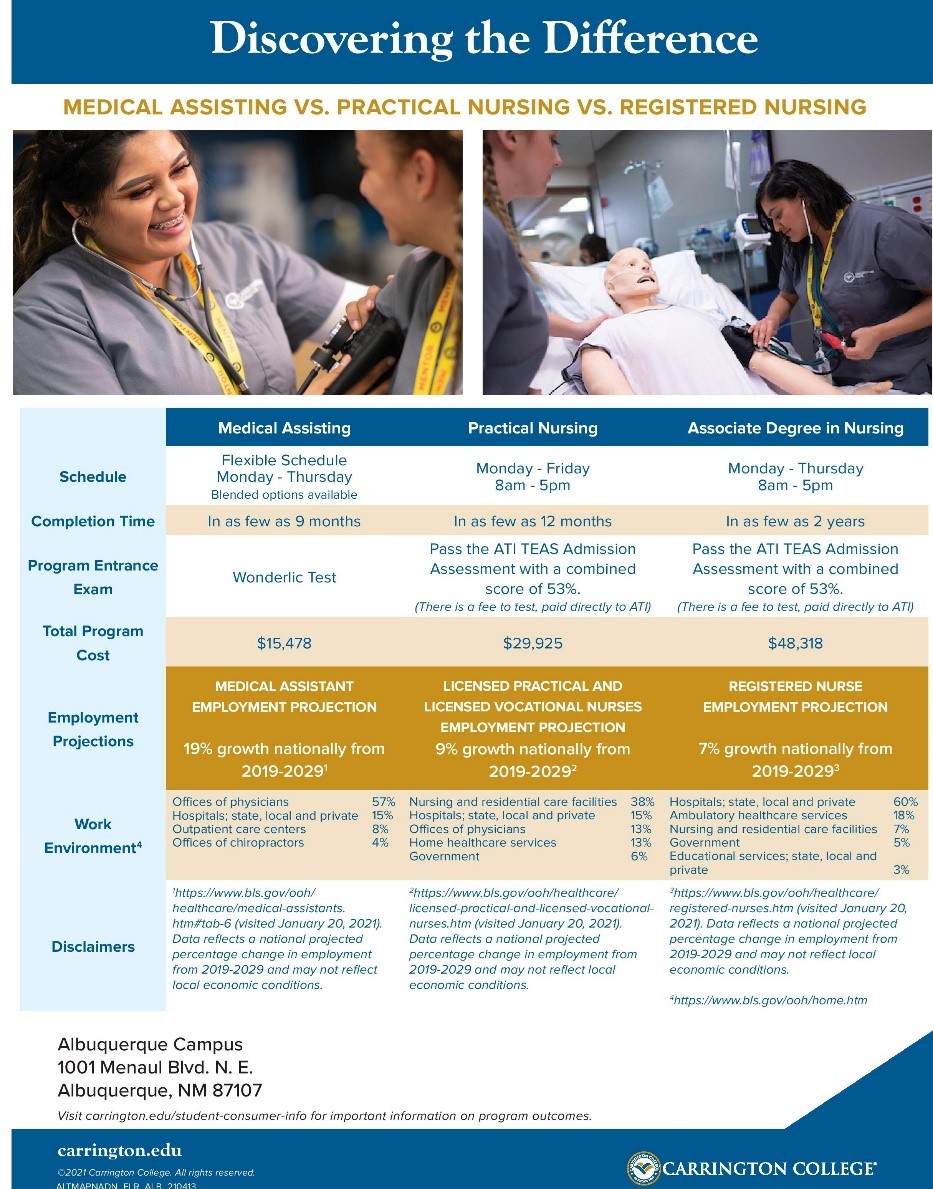
Students who earn an ADN qualify to take the National Council Licensure Examination for RNs (NCLEX-RN), which allows graduates to become licensed RNs. These RNs examine patients’ medical records, track symptoms, administer medication, and collaborate with patients’ healthcare teams.
The demand for nursing professionals continues to grow, creating diverse opportunities for candidates who earn either a Practical Nursing certificate, an Associate Degree in Nursing, or a Medical Assisting Certificate. Each of these career paths offer several advantages so we created a helpful infographic below that highlight their differences. Prospective nurses should consider their professional goals to determine which path is right for them.