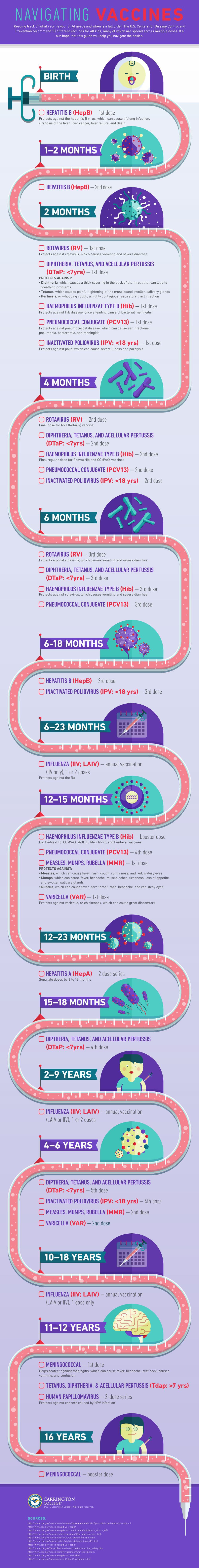
Childhood Vaccine Checklist
Did you know that the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend 13 different vaccines for all kids from birth to 18? What’s more, many of them are spread across multiple doses, over multiple months, or even years. That’s a lot to remember… so we put together this guide to help.
The infographic below maps out the CDC recommended vaccine journey for your child from birth through their late teens. We hope it helps you navigate your way.
BIRTH
– HEPATITIS B (HepB) – 1st dose. This vaccine protects your child against the hepatitis B virus, which can cause lifelong infection, cirrhosis of the liver, liver cancer, liver failure, and death.
1–2 MONTHS
– HEPATITIS B (HepB) – 2nd dose.
2 MONTHS
– ROTAVIRUS (RV) – 1st dose. This protects against rotavirus, which causes vomiting and severe diarrhea.
– DIPHTHERIA, TETANUS, & ACELLULAR PERTUSSIS (DTaP: <7yrs) – 1st dose. This protects against:
- Diphtheria causes a thick covering in the back of the throat that can lead to breathing problems.
- Tetanus, which causes painful tightening of the muscles.
- Pertussis, or whooping cough, a highly contagious respiratory tract infection.
– HAEMOPHILUS INFLUENZAE TYPE B (Hib) – 1st dose. This protects against Hib disease, once a leading cause of bacterial meningitis.
– PNEUMOCOCCAL CONJUGATE (PCV13) – 1st dose. This protects against pneumococcal disease, which can cause ear infections, pneumonia, bacteremia, and meningitis.
– INACTIVATED POLIOVIRUS (IPV: <18 yrs) – 1st dose. This protects against polio, which can cause severe illness and paralysis.
4 MONTHS
– ROTAVIRUS (RV) – 2nd dose. The final dose for RV1 (Rotarix) vaccine which was given at 2 months.
– DIPHTHERIA, TETANUS, & ACELLULAR PERTUSSIS (DTaP: <7yrs) — 2nd dose.
– HAEMOPHILUS INFLUENZAE TYPE B (Hib) – 2nd dose. This is the final regular dose for PedvaxHib and COMVAX vaccines.
– PNEUMOCOCCAL CONJUGATE (PCV13) – 2nd dose.
– INACTIVATED POLIOVIRUS (IPV: <18 yrs)- 2nd dose.
6 MONTHS
– ROTAVIRUS (RV) – 3rd dose. This is the final dose for RV5 (RotaTeq) vaccine.
– DIPHTHERIA, TETANUS, & ACELLULAR PERTUSSIS (DTaP: <7yrs) – 3rd dose.
– HAEMOPHILUS INFLUENZAE TYPE B (Hib) – 3rd dose. The final regular dose for ActHIB, MenHibrix, and Pentacel vaccines.
– PNEUMOCOCCAL CONJUGATE (PCV13) – 3rd dose.
6-18 MONTHS
– HEPATITIS B (HepB) – 3rd dose.
– INACTIVATED POLIOVIRUS (IPV: <18 yrs) – 3rd dose.
6–23 MONTHS
– INFLUENZA (IIV; LAIV) – Annual vaccination (IIV only), 1 or 2 doses. This protects against the flu.
12–15 MONTHS
– HAEMOPHILUS INFLUENZAE TYPE B (Hib) – Booster dose. This is for PedvaxHib, COMVAX, ActHIB, MenHibrix, and Pentacel vaccines.
– PNEUMOCOCCAL CONJUGATE (PCV13) – 4th dose.
– MEASLES, MUMPS, RUBELLA (MMR) – 1st dose. The MMR vaccine protects against:
- Measles, which can cause fever, rash, cough, runny nose, and red, watery eyes.
- Mumps, which can cause fever, headache, muscle aches, tiredness, loss of appetite, & swollen salivary glands.
- Rubella, which can cause fever, sore throat, rash, headache, and red, itchy eyes.
– VARICELLA (VAR) – 1st dose. This protects against varicella, or chickenpox, which can cause great discomfort.
12–23 MONTHS
– HEPATITIS A (HepA) – 2 dose series. Separate doses by 6 to 18 months.
15–18 MONTHS
– DIPTHERIA, TETANUS, & ACELLULAR PERTUSSIS (DTaP: <7yrs) – 4th dose.
2–9 YEARS
– INFLUENZA (IIV; LAIV) – Annual vaccination (LAIV or IIV), 1 or 2 doses.
4–6 YEARS
– DIPTHERIA, TETANUS, & ACELLULAR PERTUSSIS (DTaP: <7yrs) – 5th dose.
– INACTIVATED POLIOVIRUS (IPV: <18 yrs) – 4th dose.
– MEASLES, MUMPS, RUBELLA (MMR) – 2nd dose.
– VARICELLA (VAR) – 2nd dose.
10–18 YEARS
– INFLUENZA (IIV; LAIV) – Annual vaccination (LAIV or IIV), 1 dose only.
11–12 YEARS
– MENINGOCOCCAL — 1st dose. This helps protect against meningitis, which can cause fever, headache, stiff neck, nausea, vomiting, and confusion.
– TETANUS, DIPHTHERIA, & ACELLULAR PERTUSSIS (Tdap: >7 yrs)
– HUMAN PAPILLOMAVIRUS – 3-dose series. This protects against cancers caused by HPV infection.
16 YEARS
– MENINGOCOCCAL – Booster dose.
SOURCES:
http://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/schedules/downloads/child/0-18yrs-child-combined-schedule.pdf
http://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/vpd-vac/hepb/
http://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/vpd-vac/rotavirus/default.htm?s_cid=cs_074
http://www.cdc.gov/vaccinesafety/vaccines/dtap-tdap-vaccine.html
http://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/vis/vis-statements/hib.html
http://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/vis/vis-statements/pcv13.html
http://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/vpd-vac/polio/
http://www.cdc.gov/flu/professionals/vaccination/vaccine_safety.htm
http://www.cdc.gov/vaccinesafety/vaccines/mmr-vaccine.html